Research Area
+
Ratiometric fluorescence based chemosensor for the chiral recognition of carboxylates
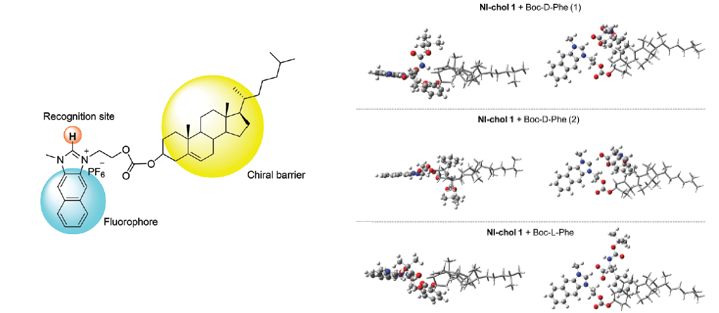
Fluorescence chemosensors to sense chiral molecules have been actively studied in recent years. In the current study, we report naphthoimidazolium-cholesterol derivative (NI-chol 1) as a fluorescence based chemosensor for chiral recognition, in which naphthoimidazolium serves not only as fluorophore but also as a recognition moiety for anions via imidazolium (C-H)+--anion binding and the cholesterol unit acts as a chiral barrier. In particular, NI-chol 1 displayed unique and distinct ratiometric changes with Boc-D-Phe, on the other hand, Boc-L-Phe induced a negligible change. Furthermore, distinct downfield shift (from 9.64 ppm to 9.96 ppm) of the imidazolium C-H peak were observed for Boc-D-Phe (5 eq.) with severe broadening, which indicates strong ionic hydrogen bonding between the C-H proton and carboxylate.